Q 1: - What precautions should be taken while collecting water samples from tap for Bacteriological testing?
Answer: - The precautions to be observed while taking water samples for bacteriological test from a tap are as under. Only sterilized bottles with lid should be used. The paper cover from the sterilized bottle should be removed just before taking samples. The stopper/lid should be removed just before filling the bottle. The stopper/lid should be held from the top while the bottle is being filled. Contamination while filling the bottle must be avoided. The mouth of the tap from which the sample is taken should be heated by a spirit lamp for three minutes. Water shall than be allowed to flow freely for 5 minutes before sampling. Bottles containing samples of water should be properly labeled, packed around with Ice and saw dust and sent without any delay to reach the DMO for examination.
Q 2: - List out the division of responsibilities for prevention / reporting among the various staff in regard to new Encroachment.
Answer: - 1. Within station premises: Lies with the Station master jointly with concerned RPF inspector and senior most RPF official at that station where no RPF inspector is posted.
2. Within / around the colony premises : Lies with the concerned Section Engineer works jointly with concerned RPF inspector and senior most RPF official at that station where no RPF inspector is posted.
3. In between stations: Lies jointly with concerned Section Engineer works/ P.way and RPF official.
4.In Loco sheds: Lies jointly with the nominated section Engineer of the loco shed and RPF Inspector.
5. In carriage & Wagon depots: Lies jointly with nominated section Engineer of the depot and RPF official. 6 In workshops: Lies jointly with nominated section Engineer (of the department to which the workshop belongs) of the Workshops and RPF official.
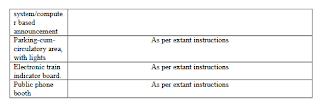
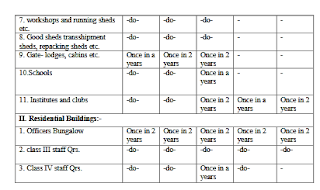
Q.No.3 (A) Describe minimum passenger amenities for deferent classes of railway stations including adarsh, model and modern stations. Minimum essential amenities. Availability of these amenities at the prescribed scale will have to be ensured.
MINIMUM ESSENTIAL AMENITIES AT EACH CATEGORY OF STATIONS.
1. External painting of high rise building involves more effort, time and risk due to requirement of high scaffolding and other temporary arrangement. It is there for desirable that the exterior painting in these building should last more than 5 years without losing sheen. Exterior wall paint should be resistant to algae, fungus, moss growth, ultraviolet rays, etc. it should be capable to fill up micro cracks on wall surface and should not allow dust/ pollutant s to adhere to its surface.
2. Contrary to this , useful life of waterproofing cement paints is very less. These paints lose their sheen and look shabby in a short period of time and often require painting every year/ alternate year depending upon climatic conditions, dust and pollution etc.
3. In case exterior wall painting of old high rise buildings (G+4 & above), the old paint should be removed completely by scraping . Plastered surface may need repair/ re-plastering . Depending upon the surface condition. Leakage, dampness, etc. has to be completely attended. If needed, thin layer of white cement based putty can be applied on the plastered surface to fill mirror cracks/ crevices in the wall surface and reduce seepage & surface irregularities. These activities can be done under relevant items of Northern Railway USSOR/Non schedule items. Subsequently, painting can be done with premium acrylic smooth exterior paint with silicon additives as per NR-USSOR Item No. 115180.
4. It is important that to get better quality, paints from very reputed brands only should be used. For guidance, some of the reputed brand names are dulux, Asian brochures, regarding application methodology, should be followed for getting desired performance.
5. Such “premium Acrylic smooth exterior paints with silicon additives” are expected to last in serviceable condition for about 5 years, if painted after proper surface preparation. In case, re- painting before 5 years is required o condition basis, Pr. Chief Engineer’s prior approval should be obtained. 6. In case of buildings having floors less thanG+4, but otherwise important in \character, such exterior wall painting , if required, can be done, with the approval of DRM.
Q.No.3(d) Explain works certificate to be issued to artisan’s staff to be deployed by contractors on works site by respective ADENs. Before the artisans are allowed on the job at site, the ASEN concerned shall examine their training certificate and or works experience certificate mentioned artisan staff on a particular railway work. Any artisan without “permit to work certificate” by the ADE in charge of the work shall not be deployed at the work site. “The contractor shall place and keep on the works at all times efficient and competent staff to give the necessary directions to his workmen and to see that they supervisors, workmen and labourers in or about the execution of any of these works as are careful and skilled in the various trades”. Due to lack of emphasis on deployment of adequately skilled staff, the quality and workmanship of works suffer so also the life of assets. As such for all the contracts under execution or to be awarded in future, it should be ensured that any artisan deployed by the contractor/out sourced agency, shall have any of the following skills certificate and or experience certificate:
i. Minimum three years of experience of having worked satisfactory for similar skill trade at any important site with reputed contractor / outsourced agency.
ii. Certificate of excellence by railway officer(minimum ADEN level).
iii. Certificate of training in particular trade for ITI or National Skilled Development Corporation (NSDC) or any similar recognized Institution for training in that particular trade. The above experience/ skills certificate criteria shall be applicable for all artisans like mason(of concerned skill e.g. mason skilled for brick work and mason skilled for tilling work are different sills), fitter, blacksmith, painter (of concerned skill). Whitewasher, carpenter, receptionist/ supervisor/housekeeping staff etc.
Question.4: What are the various planning aspects for planning Railway Staff Colonies?
Answer:- For Planning of railway staff colonies, following factors should be considered.
a) Orientation of buildings:- The Chief aim of orientation of buildings is to provide physically and psychologically comfortable living inside the building by creating conditions which suitably and successfully ward off undersirable effects of severe weather to the best possible extent. Prevailing Winds and relative humidity
b) In the coastal areas, because of less diurnal variation of temperatures along with high humidity, the emphasis should be on prevailing winds. The best orientation from solar point of view requires that the building as a whole should receive the maximum solar radiation in winter and the minimum in summer.
c) Water supply, drainage and sewerage system:- Adequate water supply and sullage and storm water drains should be provided. The water supply system should be designed on the basis of at least 200 litres/person/day (which includes 45 litres for flushing requirements) due allowance being made for gardens. Where common hydrants are provided, these may be equipped with suitable anti-waste water taps. For multi-stories builds, necessary static tanks may be provided for fire fighting arrangement in accordance with the regulations laid down. Where water borne sewerage/exists in the vicinity, open drains and soak-pits should be dispensed with and an adequate underground system provided. For colonies provided with adequate piped water supply with overhead storage facilities and where no sewerage system exists in the vicinity, an under ground sewerage system with one or two septic tanks according to the layout of the ground should be provided. Guidelines for the selection of an appropriate sanitation system are given. Groups of latrines or urinals should not be located within 15 meters of living quarters, 30 meters of any cook house or food stall, 45 meters of any well supplying drinking water and should be located away from public buildings adjoining railway colonies.
d) DUSTBINS:- These should be conveniently located with respect to the quarters and regularly cleared by the conservancy staff. In the case of multi storied buildings garbage chutes may be provided with opening in each floor with arrangements for closing the openings.
e) SHADY TREES:- Shady trees like Gulmohur, Neem should be provided along service roads at close intervals. Such trees should be provided along the periphery of parking areas and in the circulating areas in railway stations. Some ornamental trees like Alstonia, Kachnar, Bottlebrush, Cassia, Silver Oak, Mulsari, Plumerica, Ashoka and shrubs like, Chandani, Gardinia, Chinese Orange and Jatruca may also be plated. For beautification of circulating areas of stations, service of the Guardens may be maintained in circulating areas through voluntary agencies or business houses on
terms and conditions to safeguard the interest and rights of the railways.
f) PLAY GROUNDS FOR CHILDRENS:- An open space at an appropriate place in the colony may be left for entertainment and sports of the employees and their wards.
Question.5.: What is controlled concrete? Differentiate it from ordinary concrete. Generally what type of concrete mix are used for various structures.
Answer:- Types of Concrete:-
Ordinary concrete: The concrete, in which no preliminary test are performed for designing the mix, is called ordinary concrete. Controlled concrete: The concrete, in which preliminary tests are performed for designing i.e. the mix, is called controlled concrete. The controlled concrete described as M10,M15,M20,M30,M35 & M40 etc. depending upon characteristic strength of concrete. General Concrete Mix for Various Purposes.
Q.6. Define Earnest Money, Security Deposit and performance Guarantee. In which form Earnest Money Deposit, Security Deposit and Performance Guarantee should be submitted. Ans. EARNEST MONEY: Earnest Money is the amount asked from the participating tenderer in token of the genuine interest in the work on the part of the tenderer. On acceptance of the offer, total EMD becomes part of the security deposit for the performance of the contract. The Earnest Money Deposit(EMD) of unsuccessful tenderer is returned immediately on finalization of the tender. In case of withdrawn of the offer after opening of the tender but before finalization of the tender within validity period, EMD is forfeited. The cost of work, on which EMD is calculated should be realistically assessed considering the prevalent market rates. The scale of EMD is given below:
Value Of The Work Earnest Money Deposit (EMD)
A. For works estimated to cost 2% of the estimated cost of the work upto Rs.1 Crore
B. For works estimated to cost Rs.2 lakh plus ½% (half percent) of the more than Rs.1 Crore 'excess of the estimated cost of work Beyond Rs.1 Crore subject to a maximum of Rs.1 Crore '
The earnest money shall be rounded to the nearest Rs.10.
SECURITY DEPOSIT: It is the amount to be deposited by the successful tenderer as a token of the guarantee for the due and faithful fulfillment of a contract. The scale of Security Deposit is as given below:
Q.8. Describe the procedure for construction of houses for public sector undertaking under Ministry of Railway. Ans. Following conditions for const. of houses for public sector undertaking under ministry of Railways to be considered. There is general shortage of houses for officers and it has been decided that Railway PSUs may be allowed to construct houses on Railway land to overcome the shortage of houses on terms and conditions as mentioned below:-
i) Of the total number of flats constructed by Railway PSU, 50% will be for use by the Railway Administration and the remaining 50% will be licensed to the Railway PSU at normal license fee of Rs. 1000/- per annum per house, which may be paid annually.
ii) The Railway PSU concerned will bear full cost of construction on Railway land. The developments of surroundings and provision of services like road, water/electric connections, telecom and drainage and lifts etc. would also be provided by the PSU constructing the quarters.
iii) Ownership of the land and structure thereon will continue to be with the railways ad Railway will only license out 50% houses to the PSU. PSU at no stage will sell/Sublet for transfer these flats or any of the services to any other individual/authority.
iv) Maintenance of the flats licensed to the PSU will be done by the concerned PSU. It should be ensured that proper maintenance to be done by PSUs so that at the time of handing over these houses to the Railways, they are in safe condition as at the time of aging over except the natural aging. All the taxes payable on these flats to the concerned civil authority will also be paid by PSU. The electric and water charges should be recovered as per rules from the officers of PSUs and remitted to Railways.
v) No structural change whatsoever will be made by the PSUs in the flats.
vi) These flats will be licensed for a period of 30 years from the date of handing over of the flats to the PSU or till such time it exists or remains attached to the Ministry of Railways, whichever date falls earlier. After this period, the flats allotted to the PSU will be taken over by the Railways without any compensation/payment whatsoever to the PSU.
vii) Railway will have unrestricted and unconditional authority to enter the premises by its
authorized representative for inspection or for safety of for any other purpose as and when required.
viii) These houses will be allotted only to railway officers on dep8tatiojn ot the concerned PSUs or who have come on absorption. The allotment and retention of these houses will be governed by the Railway rules and consultants/Advisers to PSUs will not be eligible.
Q.9. What are the various planning aspects for planning New Railway colonies in Metro cities. Ans. For Planning of railway staff colonies, following factors should be considered :
i) Orientation of buildings :- The chief aim of orientation of buildings is to provide physically and psychologically comfortable living inside the building by creating conditions which suitably and successfully ward off undesirable effects of severe weather to the best possible extent.
ii) Prevailing Winds and Relative humidity In the coastal areas, because of less diurnal variation of temperatures along with high humidity, the emphasis should be on prevailing winds. In other areas, the emphasis should be on protection from solar radiation. The best orientation from solar point of view requires that the building as a whole should receive the maximum solar radiation in winter and the minimum in summer.
iii) Water supply, drainage and sewerage system :- Adequate water supply and sullage and storm water drains should be provided. The water supply system should be designed on the basis of at least 200 litres/person/day(which includes 45 litres for flushing requirement) due allowance being made for gardens. Where common hydrants are provided, these may be equipped with suitable anti-waste water taps. For multi-stories buildings, necessary static tanks may be provided for firefighting arrangements in accordance with the regulations laid down. Where water borne sewerage/exists in the vicinity, open drains and soak-pits should be dispensed with and an adequate underground system provided. For colonies provided with adequate piped water supply with overhead storage facilities and where on sewerage system exists in the vicinity, an underground sewerage system with one or two septic tanks according to the layout of the ground should be provided. Guidelines for the selection of an appropriate sanitation system are given. Groups of latrines or urinals should not be located within 15 meters of living quarters, 30 meters of any cook house or food stall, 45 meters of any well supplying drinking water and should be located away from public buildings adjoining railway colonies.
iv) DUST BINS: These should be conveniently located with respect to the quarters and regularly cleared by the conservancy staff. In the case of multi stories buildings garbage chutes may be provided with opening in each floor with arrangements for closing the openings.
v) SHADY TREES: Shady trees like Gulmohur, Neem should be provided along service roads at close intervals. Such trees should be provided along the periphery of parking areas in railway stations. Some ornamental trees like Alstonia, Kachnar, Bottlebrush, Cassia, Silver Oak, Mulsari, Plumeria, Ashoka and shrubs like Chandani, Gardinia, Chinese Orange and Jatruca may also abe planted. For beautification of circulating areas of stations, service of the Gardens may be maintained in circulating areas through voluntary agencies or business houses on terms and conditions to safeguard the interest and rights of the railways.
vi) PLAY GROUNDS FOR CHILDREN: An open space at an appropriate place in the colony may be left for entertainment and sports of the employees and their wards.
Q.10(a). What is the main cause of damaging the sunshades in old building? What precautions to be taken for providing RCC sunshades in new building construction?
(b) What is main cause of roof leakage and what are the remedial measures in old flat roofs.
( c) What precautions to be taken when construction of new buildings, that the roof leakage problem may not arise?
(c ) Explain water cement ratio, How the water cement ratio effects the strength of concrete.
(d) Explain, design mix concrete and nominal concrete etc.
(a) What are the main causes of damaging of sunshades in old buildings. What precautions to be taken for providing RCC sunshades in new building construction. Ans. Mostly it is seen that the sunshades of old building starts damaged after few years of construction. The followings are the main cause.
I. The top surface of sunshade having not proper slope due to which the rain water stagnating on the top surface.
II. Lack of compaction of sunshade during casting.
III. Binding of reinforcement in wrong position or-mis-placing of reinforcement during casting. The precautions to be taken while casting a sunshade in new building.
I. The shuttering of sunshade to be done more causiorsly and totally leak proof. The compaction of sunshade to be done with shutter vibration, because due to less thickness of concrete, the needle vibrator is not fruitful to compact the concrete.
II. The reinforcement (main) to be placed on top surface and ensured during casting that it will not misplaced.
III. The top surface to finished sloppy as the water cannot stagnate on surface.
(b)Main cause of roof leakage.
I. Poor slope of top surface of roof.
II. Damaging and erosion of top surface treatment.
III. Badly provided khuras.
IV. Badly provided CC bata.
V. Leakage from sewer and drainage pipe and traps laid in roof.
Precautions to be taken while construction of new building.
I. The shuttering of roof to be done having camber as per specification, so that during casting of slab the depression in roof may not arise. A slight depression in top surface of roof is very harmful although.
II. The casting of khura to be done cautiously with zero tolerance and the rain water to be fixed properly.
III. The CC bata to be done prior to parapet plaster and as per specification.
IV. Minimum 1:4 slpe to be provided in top surface of roof treatment.
V. The over head tanks (if required to be placed on roof) to be placed on proper plate form and nearly to khura.
(c)Water cement ration:- The ratio of the weight of water, to weight of cement used in a concrete mix is termed as water cement ration. As a results of experiments, it is observed that for a given proportion of ingredients in a concrete mix, there is almost a fixed amount of water (optimum) which gives maximum strength. A small variation in qty of water causes much wider variation in the strength of concrete. When the water comes. With contract of cement particle, and react with cement particle some roofs are generated from the cement particle. These roofs are binding the particle of ingredient of concrete. If we mix less water from optimum Qty. of water, the all roots can not generate and the concrete will not gain proper strength, but if we add more water than optimum requirement, the roots become diluted and the grip of these roof become less, resulting to this the lesser strength concrete obtained.
(d)Nominal mix concrete Nominal mix concrete is used in works where the quality control requirements for designed mixes are difficult to be implemented. The nominal mix concrete can be produced by taking cement, fine aggregate and coarse aggregate in the ration of 1:n:2n for normal work. However, the ration of coarse aggregate to fine aggregate can vary from 1 ½: 1 to 2 1/2 :1 in situations where denser or more workable concrete is to be produced. Mix design concrete:- the aim of mix design is to determine the proportion in which, cement, fine sand, coarse aggregate and water should be mixed to produce concrete of required strength, workability and durability with minimum cost. When the task of deciding the proportion of the constituents of concrete is accomplished by use of certain established relationship (which are based on inferences drawn from large number of experiments) the concrete these produced is termed as design mix concrete.
Q.11(a) What are the pre fab buildings? Describe in details, what is advantage and disadvantage of these buildings?
(b) What are new building materials generally available in markets and what are the advantages over conventional building materials? (a)
Prefabricated homes, often referred to as prefab homes or simply prefabs, are specialist dwelling types of prefabricated building, which are manufactured off-site in advance, usually in standard sections that can be easily shipped and assembled. Some current prefab home designs include architectural details
inspired by postmodernism or futurist architecture Advantages The advantages of using prefabrication in housing are that:
• prefabricated components speed up construction time, resulting in lower labour costs;
• prefabrication allows for year-round construction;
• work is not affected by weather delays (related to excessive cold, heat, rain, snow, etc.);
• the mechanization used in prefabricated construction ensures precise conformity to building code standards and greater quality assurance;
• there are less wasted materials than in site-built construction;
• there is less theft of material/equipment (and less property damage due to vandalism);
• materials are protected from exposure to the elements during construction;
• worker safety and comfort level are higher than in site-built construction;
• computerization of the production process permits a high degree of customization, at an affordable cost;
• quality control and factory sealing and design can ensure high energy efficiency; and
• cost savings through prefabrication can reduce the income required to qualify for a high ratio mortgage by up to one third compared to a conventionally built home of the same size.
DISADVANTAGES
The issues related to using prefabrication in housing are that:
• many municipalities zone against manufactured housing because of earlier perceptions created by trailer parks;
• concerns have been raised by local and regional governments with regard to whether the taxation paid by manufactured homes is sufficient to offset public costs such as schools;
• the requirement to transport manufactured homes or modules to their intended site can mean that prefabrication potential may be limited for infill projects in inner city areas; and
• Increased production volume is required to ensure affordability through prefabrication.
(b) New Bldg. material: - The various new bldg material generally available in the market as
1. Sand lime/calcium silicate bricks.
2. Fly ash lime bricks.
3. Clay fly brick fly
4. Burnt clay flooring tiles.
5. Burnt clay flat terracing tiles.
6. fibrous gypsum plaster board.
7. Precast channel unit for floors/roof 8. Pre cast RC plancks & joints
9. Thin RC ribbed slab for floors & roofs.
10. Pre cast waffle unit for floor/roof.
11. Pre cast reinforced concrete panels for roofs.
12. Pre cast doubly curved shell unit for floor/roof.
13. Prefabricated brick panels for floor/roof
14. Pre cast solid cement concrete block
15. Precast concrete stone masonry block
16. Hallow & solid light for concrete block
17. RCC door & window frame
18. Ferro cement doors shutters
19. Ferro cement write tender 250-1000
20. Concrete man hole cover & frame
21. Flyash/ red mud polymer door shutter
22. Rubber wood flush door shutter.
23. Finger jointing & shaping technology
24. Micro concrete roofing tiles.
25. Ferro cement roofing channels
26. Glass fibre reinforce polymer door & door frame
27. Bamboo mat corrugated roofing sheet
28. Bamboo mat ridge cap
29. Two storey bamboo housing system
30. Pre-fab double wall composite house.
Advantages of new material over conventional material
1. New bldg. material are cost effective, environment- friendly & energy efficient.
2. These new material technology are based on agro-indistrial waste such flymesh boord bricks/block, cellnar light weight concrete, bamboo board material, bag are bond.
3. Conventional bldg. technology burnt bricks, steel, & cement utilize size large amount of non-renewable like energy, miniral top soil, forest cover etc. these are dependence on external natural and manpower, harm the locol energy & are generally polluting in nature.
4. New bldg. material are not danger to bio-reserve & are Non- polluting
5. There are self sustaining & promote self reliance 6. Uses locally available material.
7. Law in monetary cost
8. Utilize reasonable energy
Q.12(a). What is chlorination and what is the function of chlorination. Why the super chlorination is required in a water supply network?
(b) Give a reasonable estimate of daily consumption of 700 four storied colony having all desirable amenities and design the water supply network accordingly.
(a) What is chlorination and what is the function of chlorination. Chlorination:- Disinfection of water is necessary to kill pathogenic bacteria of water-born diseases to make it safe for human. Consumption where the contamination of water is suspected, water has to be sterilized to remove the bacterias which may dangerous. There is every chance of water being contaminated during distribution, especially, and generally adopted in an intermittent system of water supply where the pipe remains empty for long period, sterilization of water cab be done in a number of ways. One of most commonly used system is to add chlorine in the water supplied. This type of sterilization of water is called chlorination of water. Chlorine is available in solid, liquid and gaseous form in solid form it is available in bleaching powder and chlorine tablets.
When the chlorine is added to water, the following recttions take place
Cl2 + h2o = Hcl + Hoel Hocl ____ H+ocl.
In this chemical reaction nascent fly drogen is formed which get evaporated. Also HOcl (Hypochlorous acid) and ocl (Hypochlorite ions) are formed which are responsible for disinfection. They destroy all the bacteria and help in oxidizing matter and ammonia cal substance present in the water.
When there is epidemic in the area and the residual chlorine drops suddenly. A high dose chlorination is done( 0.50 to 2.0 ppm) depending upon the impurities this term is called super chlorination.
Assuming effacing 80%
BHP= 10/0.80=12.5Hp
Q. 13.(a) What precautions should be taken while casting of sunshades in a building to obtain dense concrete of desired strength?
Ans 13(a): General sunshades are a structurally weak link in a building and very first collapse during earth quakes.
1. Adequate cover to reinforcement should be ensured.
2. Shuttering should be of sufficient strength to with stand vibration compaction.
3. Compaction of concrete should invariably be done by vibrator.
4. Adequate water cement ratio and proper mixing of concrete should be ensured.
5. Top slope should drain out rain water immediately without ant stagnation.
(b) What precautions should be taken to avoid foul smells and seepage in toilet blocks of
buildings?.
Ans 13(b): Toilets blocks of building are observed to have seepage of water, peeling of plaster and paint and foul smells.
1. All joints in plumbing work should made water tight.
2. Proper trap should be used with WC to provide sufficient water seal. This will keep away foul smells.
3. Adequate ventilation and sunlight should be planned by providing required ventilators and exhaust fans.
4. Good quality toilets fittings which do not spill water help keep the toilet clean, dry and free from bad smell.
5. Floors should have correct slope and floor traps and drain pipes should be kept clean to carry discharge of Urinal pots and wash basins.
Q.No.14 Explain the method of construction of a subway by box pushing technique.
Ans- Box Pushing Technique, is the technique of construction of subway/under bridge, by which precast box segments of bridge are pushed under the track without disturbing the existing Railway / Road embankment by deploying adequate nos. of jacks. During execution of work by this method railway traffic is allowed to pass at restricted speed. In this method a thrust bed of suitable length is cast and thereafter R.C.C. Boxes segments are cast on thrust bed. These boxes are pushed through the Railway embankments by Jacking. The required thrust is generated through thrust bed. This method may be called safest method of crossing underground / Embankment, without disturbing overhead traffic /Structures for R.U.B. Steps involved in construction of Subway by box pushing technique.
1. Soil investigation.
2. Design of thrust bed and RCC box.
3. Excavation work and construction of thrust bed.
4. Provision of drag sheet to reduce frictional forces acting on box during pushing and thereby minimizes jacking effort and track disturbances.
5. Construction of precast boxes of suitable length on thrust bed.
6. Provision of cutting edge on front box and intermediate guiding shield on other intermediate boxes.
7. Preparation for pushing i.e. Isolation of affected length of track from LWR and imposition of speed restriction, arrangement of all necessary tools plants ,materials and labours for pushing work. CRS sanction should also be obtained before starting the pushing work.
8. Starting of pushing work and maintenance of track during pushing. Record of pushing shall be maintained in pushing register.
9. Welding of track after completion of pushing and gradual raising of Speed as per IRPWM. Approaches of bridge to be watched during monsoon and track should be frequently attended on both side approaches due to settlement of earth.
Box Pushing Operation
• To push precast box segment, reaction is obtained from thrust bed. For this, screed is dismantled at pin pocket location, pin pockets are cleaned, pins are inserted and hydraulic Jacks- 8/10 nos. are installed between pins and bottom slab of the box with packing plates and spacers.
• A 20mm thick plate is provided, butting against bottom slab of box, in front of the Jacks to avoid damage to concrete surface and uniform pressure is applied to the jacksthrough Power Pack.
• After complete push (maximum 300mm) jacks are released, and jacks again packed with
packing plates and spacers. Process is repeated till front box is pushed to required position.
• Then 2nd box segment is slewed and brought in position behind 1st box segment.
• Suitable nos. Jacks, each of 200 Tons capacity, are housed between two box segments in addition to Jacks already provided between thrust bed and 2nd box segment.
• 3 nos. Jacks, each of 100 Tons capacity, are provided in 3 slots made in each side walls to
facilitate correction of line and level of box during pushing.
• Earthwork is now done in front of 1st box segment and it is pushed.
• Thereafter, jacks housed between two box segments are released and then 2nd box Segment is
pushed.
• Process is repeated till both the box segments are pushed to required position.
• Cutting Edge is dismantled & front face of 1st box segment is cast in plumb.
Precautions
1. Pushing shall be done only in presence of competent Railway P Way and works Engineer, who shall be in touch by walky talky/mobile phone.
2. At least 3 nos. Walkie -Talkie sets to be provided at site for effective communication between Power Pack Operator, SE/Works and SE/P.way.
3. Adequate work force inside the box for earth cutting and on the track for maintenance should be available before starting the pushing.
4. Proper protection of track should be done before starting the pushing.
5. No pushing should be done during passing of train. Pushing should be done in day
hours.
6. Train shall be allowed to pass only after correcting the disturbed track by P way staff.
7. Earth cutting should not be done beyond the tip of top cutting edge (i.e. tip of cutting
edge must always remain buried in earth) to avoid collapsing of earth.
8. Soil nailing should be done in case of sandy and cohesion less soil in the embankment.
9. Safety equipment such as safety belts, helmets, reflective jackets should be provided to the workers
10. After closing of the day’s work earth cut embankment should be supported by providing earth filled bags to prevent any chance of collapsing of earth due to
movement of trains.
11. All consumables such as hydraulic oil and spare parts of jack pipes fittings should be kept available at site.
12. Adequate nos. of jacks, based on weight of box and loading capacity of jack should be utilized for pushing work.
13. Constant watch should be kept on the pressure gauge of power pack during pushing and it should be ensured that pushing should be stopped when pressure gauge shows the reading near 80% of the max pressure, to avoid busting of pipe and fittings.
14. Additional jacks should be provided in wall and roof to correct the horizontal and vertical misalignment of the box.
15. Level and alignment of the box should be checked frequently with the help of dumpy/auto level and theodolite.
Q.No.15 what precaution is to be taken during construction of LHS by cut and cover method? LHS may be constructed at level crossings having following conditions:-
I) Accident prone LC’s where visibility is not clear
II) Where embankment height is 3 meter or more.
III) Where ground water level is not high.
Steps involved in execution: -
1. Soil investigation of the proposed LHS site.
2. Casting of box as per approved RDSO drawing.
3. Casting of slabs as per approved drawing.
4. Obtaining CRS sanction if manned level crossing is involved.
5. Imposing speed restriction of 20 KMPH one day prior to traffic block.
6. Placing the box segments under track in mega traffic block.
7. Normalization of speed restriction. Approaches of LHS should be kept under observation during monsoon and frequent attention would be required due to settlement of earth in approaches.
Tools and equipment required at site:-
I) 150 MT capacity crane - 02 Nos. +01 No standby
II) Poklain - 02 Nos. +01 No. standby
III) JCB - 02 Nos.
IV) Tippers - 02 Nos.
V) Water Tanker - 01 Nos.
VI) Gas Cutting and welding set - 01 Nos. Sufficient manpower is also required for track and Works by the agency to execute the work.
Pre block activities
I) Demarcation at site: - Demarcation at site of proposed LHS is done and points for cutting of track are marked with paint taking side slope into account.
II) Imposition of speed restriction and cutting of track rails: - Rail cut is made in track after imposition of speed restriction and 1 mtr fish plate is provided on all four joints.
III) Placing the precast box segments and slabs as near as possible to the proposed alignment with the help of 150 MT capacity crane.
IV) Adequate qty of ballast may be procured to make good the deficiency after block.
During block activities
I) Track dismantling and removal of ballast: - As soon as the block is permitted the fish bolts of all the joints are opened and track is lifted with the help of crane and placed at suitable place. Ballast is removed and placed within at suitable place so that it may be used at the time of restoration work.
II) Earth cutting: - Earth cutting will be done with the help of poklain from both ends and JCB. A suitable side slope is maintained to suit the local condition of earth. After completion of earth cutting up to desired level , Earth surface is leveled and rammed to obtain uniform level.
III) Sand filling: - Approx 150 mm thick layer of sand is provided over a leveled and compacted earth surface.
IV) Placing of slab: - Precast slabs are lifted with the help of crane and placed over leveled bed of sand at proper alignment of LHS. The joints of slabs are filled with cement sand mortors .
V) Box Placing:- The precast RCC boxes are placed over precast slab with the help of crane in proper alignment.
VI) Geo membrane and Geo textile: - Geo membrane is pasted at the joints of boxes to check the seepage of water through joints of boxes and Geo Textile is provided at the surface exposed to earth and ballast to cover the top and side of boxes in order to filter the water during rain and prevent the embankment earth from flowing with seepage water.
VII) Back filling: - Back filleting is done with machine to fill the space between side of box and embankment across the track and get compacted simultaneously.
VIII) Ballast Putting: - Ballast putting is done with the help of men and machine available at site as per track profile.
IX) Track linking:-Track linking is done over spreaded ballast bed and then track is linked with the existing track. Track is attended and all parameters are checked before allowing the traffic at restricted speed.
Break up tentative time taken in all during block activities is as under :-
I) Track dismantling & ballast removal - 25 minutes
II) Earth work in cutting - 60 minutes
III) Sand filling in Bed - 15 minutes
IV) Slab Placing - 30 minutes
V) Box placing - 90 minutes
VI) Geo Textile and Geo membrane - 20 minutes
VII) Back filling - 20 minutes
VIII) Ballast putting - 20 minutes
IX) Track linking and packing - 50 minutes
Total block required = 5 hrs and 30 minutes Precautions:-
1. Earth cutting to be done properly with proper slope and care should taken that side slope may not collapsed during block.
2. All engineers and workers should wear safety helmets before allowing them to work.
3. Sand bags should be provided on all four corners of the bank to retain and support the filled earth.
4. The entire Sling should be checked before starting the block and defective ones should be replaced.
5. After linking track should packed and XL and gauge should check before allowing first trains.
6. Standby crane should be placed at such location that it may be used in case of emergency without wasting much time.
Q.16. Design a column, square in section, to carry on axial load of 5000000N. Define bearing capacity of soil, explain different bearing capacity of soil, Explain plate load test of soil.
Provide 8 mm tie reinforcement at 380 mm centre to centre i.e. the least spacing among the three criterias.
BEARING CAPACITY OF SOIL
1) Bearing capacity: The bearing capacity may be define s the ability of the soil to support the load of the structural foundations without failure or deformation.
2) Ultimate bearing capacity: the maximum load intensity transmitted by the base of the footing of a structure to the soil causing the soil mass to fail in shear, is defined as ultimate bearing capacity.
3) Safe bearing capacity: the maximum load intensity the soil can take without any risk of shear failure is called safe bearing capacity of soil. It is generally calculated by dividing the ultimate capacity by a factor of a safety. Determination of ultimate bearing capacity of soil in the field To determine the ultimate bearing capacity of soil in the field ‘Plate loading test’ is normally carried out. (IS: 1888-1962) Plate loading test: This is a simple test to determine the ultimate bearing capacity of soil in the field.
1) The test essentially consist of rigid plate placed at the foundation on level. The ultimate bearing capacity is determine by loading the plate till it starts sinking at a rapid rate.
2) The bearing plate is of square section of least 30 cm side and maximum 75 cm. the plate should have sufficient thickness to withstand the anticipated maximum load and in no case it should be less than 25 mm
3) The test pit width is kept five times the width of the plate. At the centre of the pit, a square hole of the size of the plate is made whose bottom is kept at the actual level of the fitting. The depth of the hole should be determine by the formula, Dp = D Bp B Apply a static load at the centre of the plate through a calibrated jack and the reaction is taken by a load truss.
Procedure: the following step are involved.
1. Place the plate in the hole, a seating load of 70 g/cm2 is to be applied before actual test is started.
2. Apply the load in convenient increment, one-fifth of the expected safe bearing capacity or one-tenth of the ultimate bearing capacity.
3. Observe the settlement with the help of two dial gauges fixed diametrically opposite each other, having the sensitivity of 0.02 mm.
4. Observe the settlement of each increment of load after an interval of 1,4,20,40 and 60 minutes and thereafter at hourly intervals until the rate of settlement becomes less than 0.02 mm per hour.
5. Now, apply the nest load increment till the maximum load that is applied corresponds to 1/1/2 times the estimated ultimate load or three times the proposed allowable bearing pressure.
Q. No. 17. As a AEN submit proposal for works programme 2016-2017 for construction of 100 type- II, 30 type-III and 10 type-IV quarters with justification, Abstract cost on forma chargeable Plan and covering letter addressed to Sr. DEN. (25)
Ans. The Preliminary Works Programme for the following year should be submitted by the Railways to the Railway Board by 1st week of September or such earlier date as may be laid down by the Board. Proper financial appraisal of each work should be given in the Preliminary Works Programme together with the comments of the financial adviser and Chief Accounts Officer.
The works should be arranged as per the Plan Heads. The items in the Works Programme should be grouped under the following categories while
compiling the Works Programmes :--
• (i) New Works.
• (ii) Works in Progress.
• (iii) Works approved in earlier years, which have not been actually commenced and on which no expenditure has been incurred till 30th June of the year previous to the Programme year.
• (iv) Works approved in the earlier years but estimates for which have not been sanctioned
The items in the Works Programme should be grouped under the following categories. Abstract estimate for construction of new staff qtr. In the section of ADEN/NR
Chargeable to Hand 53
Justification:- The fourth line work is in progress between JNC-PWL on TKD-PWL section and expected to complete within two years. In connection with this many staff to be deputed in the section. For this about 140 nos. staff qtr. Are to be required. Hence an estimate of Rs. 7.70 Crore have been framed for inclusion in WP 2016-17 at an earliest please.
Forwarding Letter Sr. DEN-C Subject: - Proposal for works programme 2016-17 A abstract estimate with justifications are herewith enclosed for sanction & further disposal please. DA/As above ADEN/NR
Qus. 18. What is the disinfection of water? What are the precautions to be taken in collection and transportation of water sample? When in a water sample considered to be
chemically and bacteriologically satisfactory?
Ans:- The disinfection of water has to be done to remove organisms that causes disease, before entering in to distribution system chlorination is used for disinfection of water. The water should be collected in sterilized gals stopper bottle. There should be no external contact of mouth of the bottle the bottle should be filled to about 25mm below its neck , when sample of water is taken from a tab, the mouth of the tab should be heated by a sprit lamp for 3 minute. Then water should flow for about five minute before sampling bottle is filled. The bottle should be properly labelled and backed and should be sent for testing without delay. A sample is considered chemically satisfactory when the PH value should be between 6.5 to 6.8, Hardness between 300 to 600 mg/l calcium between 75 to 200 mg/l, Magnesium between 30 to 100 mg/l, Dissolved solid between 500 to 2000 mg/l, Chloride between 250 to 1000 mg/l, Sulphate between 200 to 400 mg/l. And bacteriologically satisfactory when coliform is Nil. Water should be colour less and odour less.
Qus.20. Design of a water supply scheme for railway colony of 375 quarters. In addition there is a diesel loco shed housing 85 locos and 10 NOS subordinate offices. Workout capacity of source, pumping and storage requirement. Assume data as required.
(B) Yield from the source :- In summer season, the source should be able to supply in 8
hrs the quantity of water normally required. Yield of well, 60000/8=75000 lit/day
C. Pumping capacity requirement :- The pumping system should be able to supply the water as per the following requirement
a. Normal quantity of water requirement of 24 hrs in 12 hrs time or less 6.0 lac/12=50000 lit/hrs.
b. Maximum quantity of water requirement of 24 hrs in 16 hrs time or less
= 7,50000/16
= 45,312 lit /hrs C Future quantity of 24 hrs of water requirement in 20 hrs or less
=11,25000/20=56250 lit Taking maximum of the above 3 entries which is 56,250 lit.
Say 60000 lit per day Requirement pumping capacity
=60000 lit per hrs. And as such provide 1 service pump and



























No comments:
Post a Comment
Note: Only a member of this blog may post a comment.